Key concepts in system design:
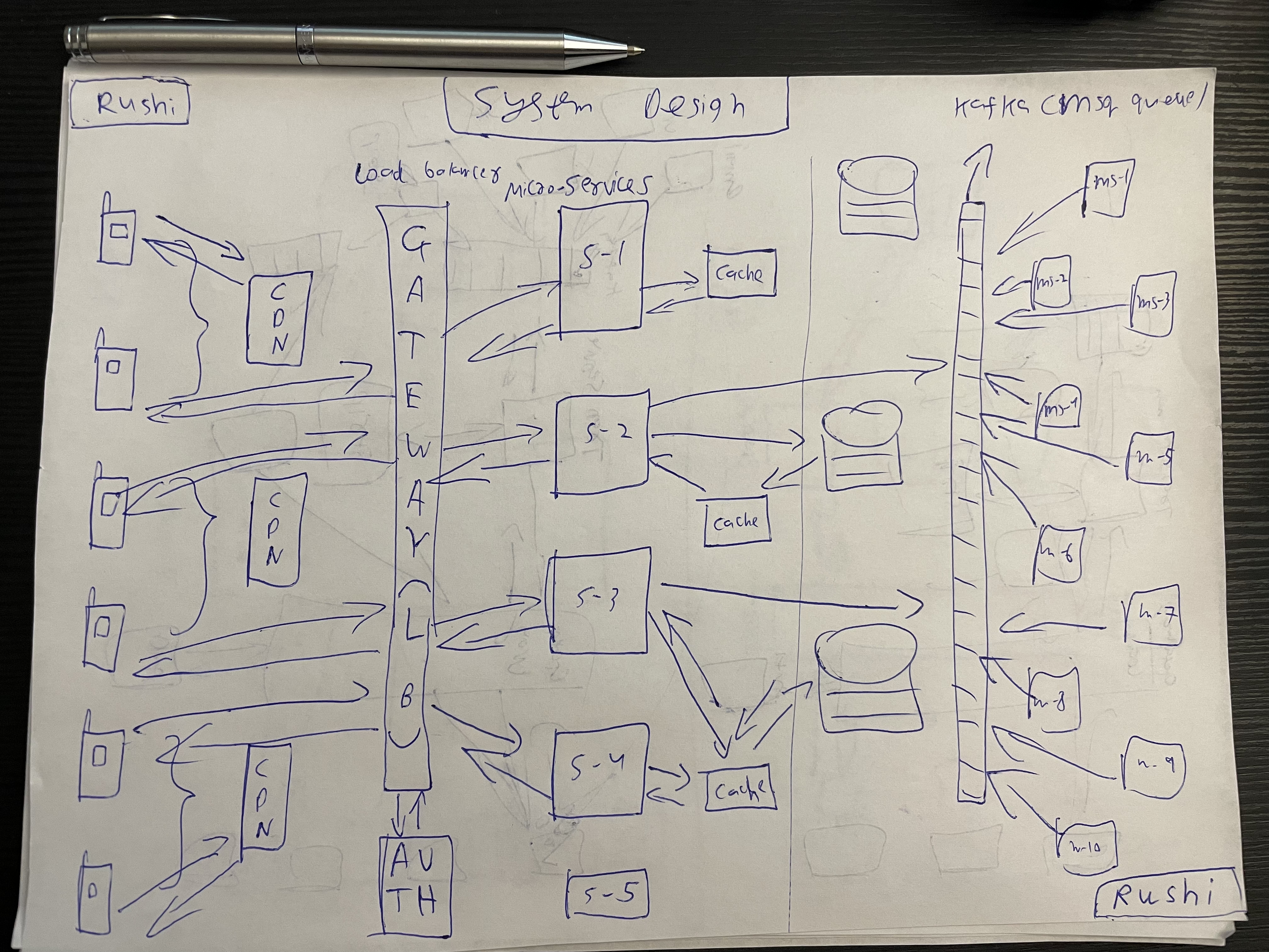
1. CDN (Content Delivery Network): A network of distributed servers that deliver web content to users based on their geographic location, improving load times, reliability, and availability by caching content closer to end-users.
2. Gateway (Load Balancer): A device or software that distributes incoming network traffic across multiple servers to ensure no single server becomes overwhelmed, improving application availability and responsiveness.
3. Authentication: The process of verifying the identity of a user or system, often using credentials such as passwords, tokens, or biometrics, to ensure secure access to resources and data.
4. Micro-services: An architectural style that structures an application as a collection of small, loosely coupled services, each responsible for a specific functionality, enabling greater flexibility, scalability, and maintainability.
5. Caching: The temporary storage of frequently accessed data in a faster storage medium (such as RAM) to reduce the time it takes to retrieve data and improve overall system performance.
6. Database (and Database Sharding): A structured collection of data stored electronically. Database sharding involves partitioning a database into smaller, more manageable pieces (shards) that can be distributed across multiple servers, improving performance and scalability.
7. Event Driven Architecture: Message Queue (Kafka) and Pub-Sub Model:
- Message Queue (Kafka): A system that enables asynchronous communication between services by queuing messages until they can be processed, providing fault tolerance and decoupling services.
- Pub-Sub Model: A messaging pattern where messages are published to topics and subscribers receive those messages based on their interests, allowing for scalable and flexible communication between distributed systems.
Rushi Patel